First, the biological characteristics of sakazakii
1 Morphological staining Enterobacter genus Enterobacteriaceae of Enterobacter sakazakii, so this strain has the basic morphological characteristics of Enterobacter: Gram-negative bacillus, with whole body pilus, no spores, and motility [1]. 2 The culture characteristics are grown on a variety of media such as common nutrient agar, blood plate, MacConkey (MAC) agar, Eosin Meilan (EMB) agar, and deoxycholic acid agar. The optimum temperature for culture is 25 to 36 °C, and it can grow at 6 to 45 °C. Some strains can grow at 47 °C [8]. After being cultured for 24 hours at 25 to 36 ° C on tryptone agar (TSA), brain heart infusion agar (BH I) and blood plate, 1.5 to 2.5 mm, yellow colonies were formed. In crystal violet neutral red bile salt dextrose agar (VRBG) can produce purple red colonies [2].
Second, the traditional detection method of sakazaki
The procedure for the detection of Enterobacter sakazakii is shown in Figure 1.
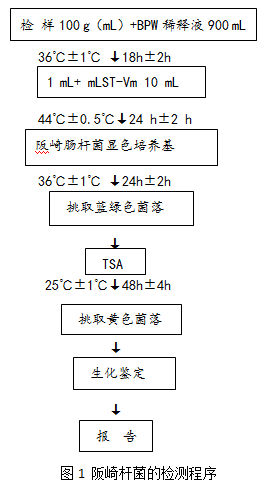 1 The basic steps are as follows: Take 100g (mL) of the test sample and add it to the Erlenmeyer flask which has been preheated to 44°C and filled with 900mL buffered peptone water. Stir slowly until it is dissolved by hand. Incubate at 36°C±1°C for 18 h± 2h. Transfer 1 mL to 10 mL mLST-Vm broth and incubate at 44 °C ± 0.5 °C for 24 h ± 2 h. The mLST-Vm broth culture was gently mixed, and each of the enriched cultures was ligated to two plates of Enterobacter sakazaki chromogenic medium, and cultured at 36 ° C ± 1 ° C for 18 h ± 2 h. Pick 1 to 5 suspicious colonies and inoculate them on TSA plates. Incubate at 25 °C ± 1 °C for 48 h ± 4 h. Yellow suspicious colonies were picked directly from the TSA plates for biochemical identification. The main biochemical characteristics of Enterobacter sakazakii are shown in Table 1. Biochemical identification kits or fully automated microbial biochemical identification systems are available.
1 The basic steps are as follows: Take 100g (mL) of the test sample and add it to the Erlenmeyer flask which has been preheated to 44°C and filled with 900mL buffered peptone water. Stir slowly until it is dissolved by hand. Incubate at 36°C±1°C for 18 h± 2h. Transfer 1 mL to 10 mL mLST-Vm broth and incubate at 44 °C ± 0.5 °C for 24 h ± 2 h. The mLST-Vm broth culture was gently mixed, and each of the enriched cultures was ligated to two plates of Enterobacter sakazaki chromogenic medium, and cultured at 36 ° C ± 1 ° C for 18 h ± 2 h. Pick 1 to 5 suspicious colonies and inoculate them on TSA plates. Incubate at 25 °C ± 1 °C for 48 h ± 4 h. Yellow suspicious colonies were picked directly from the TSA plates for biochemical identification. The main biochemical characteristics of Enterobacter sakazakii are shown in Table 1. Biochemical identification kits or fully automated microbial biochemical identification systems are available.  2 Results and report Comprehensive colony morphology and biochemical characteristics were reported, and Enterobacter sakazakii was detected or not detected per 100 g (mL) of samples. 3 Precautions (1) Disinfect the opening of the sample package and the sampling spoon before sampling. (2) The test sample should not be lower than 333g.
2 Results and report Comprehensive colony morphology and biochemical characteristics were reported, and Enterobacter sakazakii was detected or not detected per 100 g (mL) of samples. 3 Precautions (1) Disinfect the opening of the sample package and the sampling spoon before sampling. (2) The test sample should not be lower than 333g. Third, the introduction of new technology
1 Fluorescent selective medium method This method is also a method for detecting α-glucosidase activity [3]. 4-Methyl-umbelliferone-α-D-glucoside (α-MUG) was added to the nutrient agar. Enterobacter sakazakii forms yellow colonies on the medium and fluoresces under ultraviolet light. The method has good sensitivity and specificity and has been used in many countries, and has achieved stable and reliable results. 2 p-nitrophenol photoelectric colorimetry using the α-glucosidase activity of Enterobacter sakazakii to decompose p-nitrophenol-α-D-glucoside substrate, releasing yellow p-nitrophenol at 405 nm The absorbance is measured, and the presence or absence of Enterobacter sakazakii in the sample is determined based on the absorbance. The method is routine enrichment, picking suspicious colonies on VRBG or TSA plates, preparing a certain concentration of bacterial suspension and substrate to mix, and measuring colorimetrically after 37 °C for 4 h [4]. 3 Fluorescence quantitative PCR method The basic principle of fluorescence quantitative PCR technology is to add a fluorescent group in the PCR reaction system, which is a pair of suitable fluorescent substances, which can form an energy donor and energy receptor pair, wherein the donor The emission spectrum overlaps with the absorption spectrum of the receptor. When the PCR reaction gene is amplified, the fluorescence energy released by the excitation donor is absorbed by the receptor, so that the fluorescence intensity of the donor is weakened and the fluorescence intensity of the receptor is enhanced, and the fluorescence signal is strong. The weak change accumulation monitors the entire PCR reaction process in real time, and finally quantifies the unknown template through the standard curve. Real-time PCR technology has been widely used to detect a variety of food microbial contamination. SEO and so on used the partial macromolecular synthesis (MMS) operon gene sequence of Enterobacter sakazakii to establish a real-time quantitative PCR method for Enterobacter sakazakii in milk powder, which can detect Enterobacter sakazakii in 0.6-1g milk powder, and is more traditional than The culture method detection time was shortened from 6 to 7 days to 2 days. 68 strains of Enterobacter sakazakii and 55 strains of non-Sakasaki bacteria were detected without false positives and false negatives, and had good specificity.
Conclusion:
The traditional detection methods have the disadvantages of cumbersome operation and long time, and it is difficult to meet the needs of modern clinical rapid diagnosis and treatment. To understand more accurate, fast, simple, and reliable methods and techniques, science has done a lot of research on this, test methods and identification technologies are constantly developing and improving, and new progress is continuously made in practice.
ZGAR Disposable Vape
ZGAR electronic cigarette uses high-tech R&D, food grade disposable pod device and high-quality raw material. All package designs are Original IP. Our designer team is from Hong Kong. We have very high requirements for product quality, flavors taste and packaging design. The E-liquid is imported, materials are food grade, and assembly plant is medical-grade dust-free workshops.
Our products include disposable e-cigarettes, rechargeable e-cigarettes, rechargreable disposable vape pen, and various of flavors of cigarette cartridges. From 600puffs to 5000puffs, ZGAR bar Disposable offer high-tech R&D, E-cigarette improves battery capacity, We offer various of flavors and support customization. And printing designs can be customized. We have our own professional team and competitive quotations for any OEM or ODM works.
We supply OEM rechargeable disposable vape pen,OEM disposable electronic cigarette,ODM disposable vape pen,ODM disposable electronic cigarette,OEM/ODM vape pen e-cigarette,OEM/ODM atomizer device.

ZGAR Disposable Vape,ZGAR Disposable Vape disposable electronic cigarette,ZGAR Disposable Vape pen atomizer ,ZGAR Disposable Vape E-cig,disposable electronic cigarette
ZGAR INTERNATIONAL(HK)CO., LIMITED , https://www.szvape-pods.com