What is an IoT card?
An IoT card, also known as an M2M (Machine-to-Machine) card, is a specialized communication device designed to connect physical objects to the internet. These devices use various information-sensing technologies such as RFID, infrared sensors, GPS, and laser scanners to enable smart identification, location tracking, monitoring, and management of connected items. By following a contractual agreement, IoT cards allow any object to communicate and exchange data over the internet. In simpler terms, an IoT card acts as a smart mobile terminal or in-vehicle device that links people, resources, and services through a communication network, enabling efficient and targeted operations. It's a mobile communication service offered by telecom operators specifically for IoT users, built on public IoT service networks.
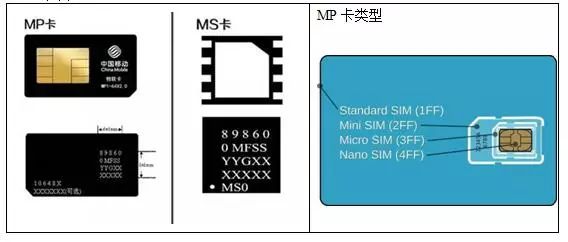
IoT cards come in different types, primarily MS cards and MP cards. MS cards are typically used for front-loading during production, while MP cards can be used both for front and back loading. Due to their compact size, durability, high temperature resistance, and long lifespan, MS cards are often found in applications like in-car systems, smart metering, and wearable technology. On the other hand, MP cards are more cost-effective and easier to install, making them widely adopted in various IoT scenarios.
Here’s a list of common sizes:
| Product Name | Package Form | Model | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| M2M Card, Io Card | MP Card (Plug-in Type) | Mini SIM Card | 25mm × 15mm |
| Micro Card | 12mm × 15mm | ||
| NANO Card | 9mm × 12mm | ||
| MS Card (Slice Type) | MS0 | QFN5×5-8 | |
| MS1 | QFN5×5-8 | ||
| MS0 | QFN5×6-8 | ||
| MS1 | QFN5×6-8 |

What is the difference between an IoT card and a SIM card?
While an IoT card looks similar to a traditional SIM card, it is essentially a traffic-only card. Although it can support voice calls and SMS, these features are rarely used due to higher costs. Therefore, it's mainly focused on data transmission. IoT cards are commonly used in mobile payments, POS machines, smart wearables, and vehicle networking, where cost-effectiveness and reliability are key factors.
Below is the network standard adopted by China's three major telecom operators:
| Network Standard | China Mobile | China Telecom | China Unicom |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2G | GSM | CDMA 1x | GSM |
| 3G | TD-SCDMA | CDMA2000 | WCDMA |
| 4G | TD-LTE | FDD-LTE |
When choosing an IoT card supplier, there are many options available in the market. Selecting a long-term stable and reliable provider requires careful evaluation based on your specific needs. Some suppliers act as resellers, focusing on short-term profit. However, a good IoT card service should offer continuous support and operational assistance through a strong platform, ensuring users can rely on their IoT cards for long-term use without worry.
YIWU JUHE TRADING COMPANY , https://www.nx-vapes.com