1. Introduction
LPHCSL (Low-Power HCSL) was developed to reduce the power consumption of conventional HCSL drivers. The main advantages of LPHCSL include better drive long-line performance, easy AC coupling, reduced PCB board area, easy wiring, and reduced material cost. This article will discuss these advantages. It is important to note that HCSL drivers and LPHCSL drivers are for HCSL receivers. Said to be the same.
2. HCSL drive structure
Figure 1 Comparison of traditional and low power HCSL drive structures
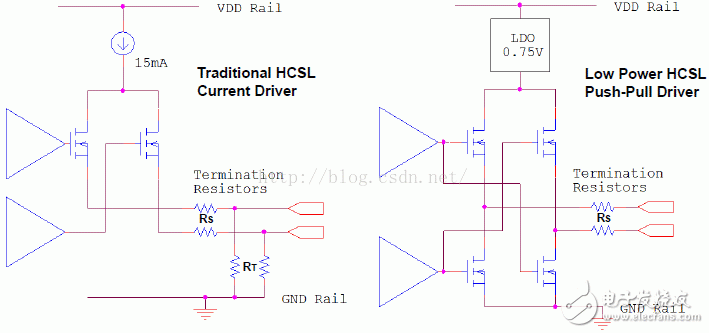
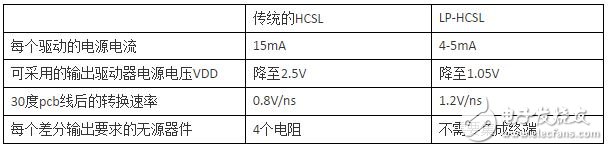
Referring to the HCSL and LPHCSL output structure diagrams of Figure 1, the conventional HCSL output is controlled by a 15mA current in the differential pair of positive and negative outputs. Obviously the power consumption is 15mA * 3.3V and about 50mW. LPHCSL is not driven by the traditional HCSL current, but is driven by a push-pull voltage with a current consumption of approximately 4 to 5 mA.
Figures 5 and 6 show the traditional HCSL and LPHCSL terminal matching methods:
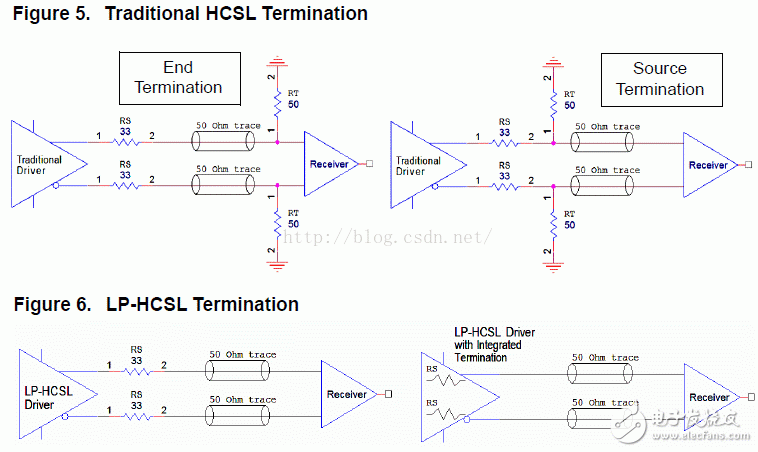
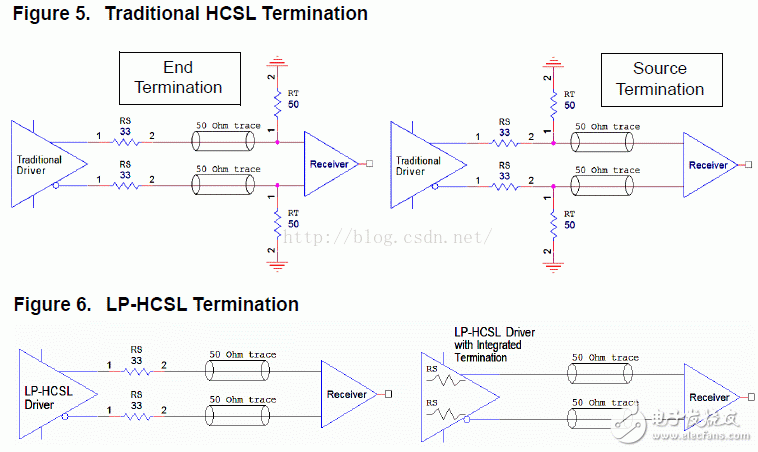
The driver itself has an output impedance of 17 ohms, so a 33 ohm resistor is required in series to match the 50 ohm transmission line. For conventional HCSL, in order to avoid excessive ringing, series resistance RS is necessary.
Some receivers may have a 100 ohm differential termination in the chip. Such receivers are usually more common because they can handle a wide range of amplitudes and common-mode voltages, as well as clock signals that may be AC-coupled. LPHCSL drivers can be stabilized. Drive dual terminals (with terminating resistors at both source and sink).
From Figure 6, we can see that LPHCSL does not require termination resistance to ground. Due to power consumption, traditional HCSL drivers cannot integrate termination resistors internally, especially when the chip has many outputs. It is clear that LPHCSL uses fewer components than conventional HCSL, reducing board area and material cost.
In principle, traditional HCSL requires DC coupling, while LPHCSL does not require DC coupling. We can connect the AC coupling capacitors to the line, which does not affect the swing and termination properties of the signal. When the traditional HCSL uses AC coupling, the DC path to the ground must be carefully considered, and additional components may be required.
The PCIe clock requires an ascending rate of 0.6V/ns to 4.0V/ns, and LPHCSL provides a higher rate of rise when driving long lines. The traditional HCSL driver relies on an external 50 ohm termination to generate the falling edge of the clock, which makes the rise/fall match very difficult because only the rising edge of the clock is controlled by the traditional HCSL output, while the LPHCSL output controls the rising and falling edges of the clock. The faster rate of rise of LPHCSL is very important when driving long lines.
3. in conclusion
LPHCSL not only significantly reduces power consumption, but also drives long lines better, saves board area, reduces cost, and makes it easier to drive AC-coupled transmission lines. LPHCSL will be used more and more widely.
Table 1: Summary of comparison between traditional HCSL and low power HCSL
48V25Ah Lithium Ion Battery,48V25Ah Lifepo4 Battery,48V Lithium Battery For Electric Scooter,48V25Ah Lithium Battery Pack
Jiangsu Zhitai New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zt-tek.com